Job
 Sterilization in a dry oven
Sterilization in a dry oven
In the world that surrounds us, there is an incredible amount of harmful bacteria and microorganisms.
Their vital activity can greatly harm the human body. Especially often, by the nature of their activities, medical workers and citizens who are being treated in hospitals and clinics are at risk. Therefore, the conditions of sterility in all medical institutions must be strictly observed. Sterilization is the complete destruction of all types of microorganisms and bacteria that can be both on the surface and inside the object being sterilized.
Read completely "
 Disinfection quality control
Disinfection quality control
Since childhood, everyone knows the expression "cleanliness is the key to health, and order, above all."
But how to check how well the disinfection of the premises is carried out? Quality control of cleaning and disinfection in any premises can be carried out in three ways:
read more »
 Prevention of occupational infection of a nurse
Prevention of occupational infection of a nurse
Any profession is associated with the risk of disease.
The reasons may be different: faulty equipment, violation of safety standards, the development of hidden diseases, non-compliance with hygiene, etc. The probability of falling into the risk zone is quite high for nurses, since by the nature of their work they work directly with sick people, blood, acute items. Read completely "
 Chemical sterilization
Chemical sterilization
Sterilization is a complex of complex measures aimed at eliminating pathogenic microflora.
It can be produced by physical or chemical action on materials. In medicine, all instruments, devices and devices that come into contact with blood, mucous membranes or wound surfaces are subjected to mandatory sterilization treatment. Read completely "
 Modern disinfectants in medicine
Modern disinfectants in medicine
Relevant and meaningful.
A problem that everyone faces sooner or later. Disinfectants, especially in medical institutions and medical institutions, where sterility and cleanliness should come first. Disinfect from all kinds of infections, viruses and fungi. For this, medical equipment, tools, as well as hands are processed and quartzization of rooms is carried out. Classes of substances:
read in full »
 The work of a nurse in the infectious diseases department
The work of a nurse in the infectious diseases department
Patients admitted to the infectious diseases department need special care, especially those who have been diagnosed with a severe form of a particular infection.
Much here depends on the nurses, whose professional skills help to properly organize the treatment process prescribed by the doctors. Read completely "
 Setting a hypertonic enema
Setting a hypertonic enema
 Easy to use and in composition, an enema is placed, including at home. It consists of a solution of magnesium sulfate 20%, it can be 30%, the temperature of the solution should be 38 ºС. The second option is to use a 10% sodium chloride solution, the people use ordinary edible salt. Be sure to pay attention to contraindications, if arterial or intracranial pressure is elevated, and if edema is observed, it is not recommended to use a water-based enema.
Easy to use and in composition, an enema is placed, including at home. It consists of a solution of magnesium sulfate 20%, it can be 30%, the temperature of the solution should be 38 ºС. The second option is to use a 10% sodium chloride solution, the people use ordinary edible salt. Be sure to pay attention to contraindications, if arterial or intracranial pressure is elevated, and if edema is observed, it is not recommended to use a water-based enema.
The very procedure for using an enema is the introduction of a prepared solution into the rectum. Penetrating inside, the solution helps to thin the feces, to facilitate its removal from the intestines. The enema acts instantly, improving the condition of a person.
An enema is prescribed for people with problematic fecal discharge. With the introduction of an enema, the patient's blood circulation volume decreases, pressure decreases.
 Caring for a patient in a coma
Caring for a patient in a coma
A coma is an unconscious state of a person in which the functions of almost all sensory organs are impaired. In a coma, inhibition of the higher nervous activity of a person is clearly expressed. The causes of this condition are circulatory disorders of the brain, diabetic or renal coma, liver dysfunction, severe thyroid disease, mushroom or gas poisoning, and so on.
Read completely "
 First Aid for Seizures
First Aid for Seizures
Seizures, causes and their manifestations
Seizures is a non-specific reaction of the body to the manifestation of external and internal stimuli, which lead to sudden attacks of muscle contraction uncontrolled by the patient, lasting for various periods of time.
Often during convulsions, patients are prone to loss of consciousness. Sources of seizures (in other words, convulsive syndrome) can vary from congenital defects, hereditary diseases and pathologies, to tumors and other acquired causes.
Such a syndrome can even be caused by a banal strong emotional overstrain and a sharp increase in the patient's body temperature (mainly when the patient is a child). Read completely "
 First aid for nosebleeds
First aid for nosebleeds
Epistaxis is the outflow of blood from the nasal cavity.
First aid for nosebleeds.
Reasons for appearance.
In healthy adults, bleeding can cause heat stroke or sunstroke (overheating of the body), as well as bruises, falls or bumps.
With a disease of the nasal cavity and sinuses or an increase in arterial or intracranial pressure. A decrease in the level of platelets in the human body (anemia, leukemia) can also provoke the appearance of bloody discharge from the nose. Among patients who visit an ENT doctor, 6-11% are people complaining of spontaneous bleeding from the nose, and 21% are hospitalized for emergency reasons, usually after an injury. Read completely "
 Emergency care for heat stroke
Emergency care for heat stroke
In the summer season, in hot weather, cases of overheating of the body are not uncommon.
People spend a lot of time outdoors, because summer is the time for holidays, which means that we eat garden plots, the sea and spend a lot of time under the scorching sun. Of course, everyone and everyone needs to know how to behave when symptoms of heat stroke appear, and what actions need to be taken. Heat stroke is the result of overheating of the body.
Read completely "
 Primary debridement (PSW)
Primary debridement (PSW)
Primary surgical treatment of a wound is a surgical operation that must be performed in a medical and preventive institution by a doctor with the qualifications of a surgeon.
The goal is to exclude suppuration of damage and create conditions for speedy healing. Read completely "
 Transfusion of blood and its components
Transfusion of blood and its components
Indications for the transfusion of blood and its components
 There are two categories of indications for the procedure of blood transfusion: absolute and relative .
There are two categories of indications for the procedure of blood transfusion: absolute and relative .
Examples of absolute indications are profuse blood loss, terminal state, shock. Relative indications include cases in which blood transfusion is only one of the components of treatment. In such situations, it is necessary to carefully consider the patient's contraindications for surgery in order to prevent complications. In acute anemia and leukemia, only erythrocyte mass is transfused. In some cases, transfusion of blood plasma is performed.
These include DIC, profuse blood loss of more than a third of the total circulating blood volume, coagulopathy, an overdose of anticoagulant drugs, a decrease in blood clotting factors (for example, with hepatitis) and some other abnormalities. Read completely "
 Determination of blood groups using coliclones
Determination of blood groups using coliclones
Zoliclones are monoclinal antibodies that are obtained from the blood of laboratory mice.
Everything is done through genetic engineering. The blood group, in our time, the ABO system, is established precisely with the help of these antibodies. Extremely large and high activity and avidity are demonstrated by coliclones, which suggests the time of arrival and the severity of the agglutination (gluing) reaction.
This technique is used only in a full-fledged laboratory.
Moreover, inside the cabinet, the temperature must be within the range starting from +15.0 and up to + 25.0 degrees Celsius. And the process of establishing a blood group can only occur with excellent lighting. Read completely "
 Determination of blood groups with standard sera
Determination of blood groups with standard sera
The determination of blood groups is based on the agglutination reaction, that is, sticking together.
Lumps form when both agglutinogen A and agglutinin alfa, or agglutinogen B and agglutinin beta, or both are present in the sample. Agglutinogens are found in red blood cells, and agglutinins are components of blood plasma. Read completely "
 Urinalysis according to Addis-Kakovsky
Urinalysis according to Addis-Kakovsky
When diagnosing pathological processes in the kidneys, an Addis-Kakovsky urinalysis is performed, which makes it possible to determine the quantitative content of formed elements in the urine (erythrocytes, leukocytes, cylinders). This research method is currently used quite rarely, however, the nurse must know the purpose of the analysis and the algorithm for the collection procedure.
Otherwise, this analysis is called a urine test using the Kakovsky-Addis method, because. it was first proposed by our compatriot, doctor, scientist and teacher Anton Fomich Kakovsky in 1910. The urine collected from the patient for 8 hours during a night's sleep was studied. In 1925, the American scientist and physician Thomas Addis recommended that the Kakovsky method be improved. At the same time, urine was collected by patients per day.
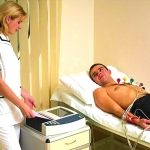
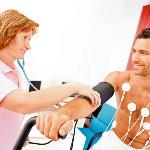
 ECG technique
ECG technique
An important skill for a nurse is the correct technique for taking an ECG (electrocardiogram). Recall that electrocardiography is a technique for recording the electrical fields of the heart that arise in the course of its activity, as well as obtaining their graphic image on paper or a display. Electrocardiography is an informative and non-invasive method for studying the work of the heart - convenient and valuable for the patient and the attending physician.
 District nurse of the polyclinic
District nurse of the polyclinic
Many polyclinics, as well as some medical units, operate on a territorial-district basis. At the same time, such a specialty as a district nurse in a polyclinic or a medical unit is very relevant. Especially in light of the fact that currently priority is given to primary care.
The main goal of the district nurse's activity is to help a doctor working in the same assigned area. The work consists of two main sectors:
 Sanbulletin on the topic "Influenza"
Sanbulletin on the topic "Influenza"
As part of health education work, every nurse is faced with the need to issue a health bulletin. During the off-season, when there is a surge in the incidence of viral infections, the sanitary bulletin on the topic “Influenza” will be relevant.
When creating such a carrier of information, it must be remembered that we are doing this work for patients - people who are most often not associated with medicine. Therefore, the language of presentation should be accessible, understandable, without an abundance of specific terms.
 Children's clinic filter
Children's clinic filter
To exclude or minimize contacts of healthy children with patients during an outpatient visit to a pediatrician, there is a filter for a children's clinic as a separate structural unit. The position of the filter worker is assigned to a middle-level medical worker with sufficient experience in pediatrics - a paramedic or a nurse.
 The work of a pediatric nurse
The work of a pediatric nurse
The work of a nurse in the children's department of a hospital is interesting and in demand, although difficult and hyper-responsible.
It is the high qualification and organization of the pediatric nurse that determines the rhythm of the department's work schedule. Patients under the age of 18 with various diseases and acute pathologies are hospitalized in children's departments. Newborns and young children may be hospitalized with relatives or guardians, more often with mothers. Read completely "
 Narcology Nurse
Narcology Nurse
The narcological hospital or narcological department is a regime, as well as psychiatric hospitals or departments. This means that there is a certain regime - the entrance doors are locked, there is no free entry and exit, the windows are barred, patients are under strict supervision or under the supervision of staff on duty. Each nurse of the narcological department must undergo training in the specialty "nursing in narcology" with subsequent certification and re-certification once every 5 years.
 The role of the nurse in disease prevention
The role of the nurse in disease prevention
The role of a nurse in the prevention of diseases of a very different nature in a wide variety of branches of medicine is great and significant. The nurse is near the patient most of her working time and much longer than the doctor. And it has the right and obligation to convey knowledge about the prevention of diseases of various organs and systems, as well as infectious diseases.
 Methods of functional diagnostics
Methods of functional diagnostics
An objective assessment of the work of various organs and systems of the body can be made by methods of functional diagnostics - the study of functions with the help of technical instruments and apparatus. Functional diagnostics helps to establish the degree of disruption in the functioning of organs and systems. Functional abilities are examined in both adults and children.
Modern medicine cannot be imagined without this section. To work in the departments and cabinets of functional diagnostics, paramedical workers who have passed the relevant specialization and have successfully completed all the examination requirements are allowed.
There are many methods by which the physiological parameters of the human body are assessed. Let's consider the most common.
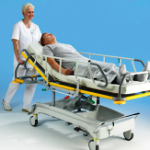
 Transportation of the patient to the department
Transportation of the patient to the department
In nursing, one of the important skills is the safe transportation of the patient to the department upon admission to the hospital, as well as to auxiliary rooms as prescribed by the doctor. The purpose of this manipulation is to create maximum rest for the patient when moving.
Depending on the severity of the patient's condition, the doctor determines the type of transportation:
- on foot;
- in a wheelchair
- on a wheelchair;
- on a stretcher;
- on hands.
 Change of underwear and bed linen
Change of underwear and bed linen
Patients in the hospital change underwear and bed linen is made in a planned manner 1 time in 7-10 days and on an emergency basis as it gets dirty. The nurse must be proficient in changing linen to ensure compliance with the patient's personal hygiene requirements.
Equipment
- A set of clean underwear and bed linen.
- Gloves.
- Bag for collecting dirty linen.
- Disinfectant container.
 Collection of urine according to Zimnitsky
Collection of urine according to Zimnitsky
To study the excretory and concentration ability of the kidneys, a Zimnitsky test is performed. Such a diagnostic procedure is prescribed for patients with kidney pathology, as well as for diseases of the cardiovascular system (IHD, hypertension) and the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus). Proper collection of urine according to Zimnitsky ensures the reliability of the result of the study. The main task of the nurse is to educate the patient in the preparation and conduct of urine collection for analysis.
 Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko
Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko
If it is necessary to quantify erythrocytes, leukocytes, cylinders (shaped elements) in the urine, a urine test according to Nechiporenko is performed. It is prescribed by a doctor when an increased number of leukocytes is detected in the general blood test , in the general analysis of urine - cylinders, and in other cases.
To obtain a reliable analysis result, the patient should be taught the preparation and direct collection of urine. The equipment for this procedure is a clean, dry jar or a plastic container with a hermetically sealed lid and a referral for research filled out in the prescribed form.
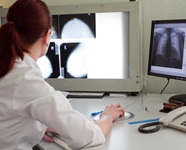
 X-ray methods of research
X-ray methods of research
X-ray methods of examination of the body help to diagnose many diseases of internal organs and systems. A nurse, depending on the position and field of work, one way or another is faced with x-ray diagnostics.
The tasks of the nurse may be to ensure the preparation of the patient for x-ray examinations, help the doctor during the procedure, or directly conduct it (X-ray laboratory assistant).
 Professional ethics of the nurse
Professional ethics of the nurse
In daily activities, according to official duties, the professional ethics of a nurse comes to the forefront of skill. It is in the observance of ethical principles in any situation that the nurse demonstrates her high professionalism.
In 1996, the Association of Nurses of Russia developed and adopted, and in 1997 approved by the Problem Commission on Nursing of the Office of Educational Institutions of the Ministry of Health, the Code of Ethics for Russian Nurses .
 Medical bioethics
Medical bioethics
The moral side of human activity in medicine is studied by medical bioethics (or biomedical ethics). The concept of "ethics" means the doctrine of morality and ethics, their meaning and purpose.
The term "bioethics" (ethics of life) was introduced into everyday life in 1969 by the American biochemist and oncologist V.R. Potter. An outstanding doctor and scientist designated by this term the ethical problems of mankind associated with the existing and probable danger to its survival in the modern Potter world. And the connection between ethics and medicine has existed for thousands of years.
 BCG staging technique
BCG staging technique
The TB vaccine is given with the BCG vaccine and is the very first vaccine that a newborn receives in the maternity hospital in the first days of his life. The BCG staging technique is not particularly difficult, but it requires the utmost care, composure and responsibility from the nurse. Only specially trained paramedical personnel are allowed to administer vaccinations.
The decoding of the abbreviation BCG in Russian sounds like “Bacillus Calmette-Guerin”, however, BCG is the “tracing paper” of the Latin abbreviation BCG, which means “bacillus Calmette-Guerin”.
 Mantoux test setting
Mantoux test setting
Tuberculin diagnostics, or Mantoux test, is carried out in order to select a contingent of patients for vaccination and revaccination of BCG, as well as to detect tuberculosis and infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Indications for Mantoux test
Appointment of a doctor in accordance with the vaccination schedule:
- from 1 to 7 years - 2 times a year (the interval between the Mantoux test is 6 months);
- from 7 years and older - 1 time per year (interval - 12 months).
- Read completely "
 Enteral drug administration
Enteral drug administration
The most convenient and painless can be called enteral administration of drugs - through the digestive tract - sublingually (under the tongue), orally (through the mouth) and rectally (through the rectum).
A significant drawback of the use of drugs per os is the possibility of destruction of active substances under the influence of the digestive juices of the gastrointestinal tract. Another disadvantage is the adverse effect on the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines. With oral administration of drugs, its relationship with the time of eating is important. There are drugs, the use of which is justified only before meals (0.5 - 1 hour) - in order to avoid their destruction and to increase absorption.
 Clinical blood test
Clinical blood test
Most often in medical practice, a clinical blood test for diagnostic purposes. A general clinical blood test includes a qualitative and quantitative study of blood cells, which include:
- erythrocytes;
- platelets;
- leukocytes;
- amount of hemoglobin;
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
Changes in the cellular composition indicate the presence of pathological processes in the human body.
 The use of rectal suppositories
The use of rectal suppositories
The use of rectal suppositories (suppositories) is indicated for diseases of the lower intestines, gynecological pathology, and also when it is impossible to administer the medicinal substance in another way.
The purpose of this procedure may be:
- the effect of the drug on the rectal mucosa;
- the introduction of the drug into the body enterally;
- rapid bowel movement.
Contraindications to the use of rectal suppositories
- Intestinal bleeding.
- Individual intolerance to the drug.
 Collection of urine for general analysis
Collection of urine for general analysis
How urine is collected for general analysis and other studies, the nurse must know perfectly. Urine for general analysis is sent to study the functioning of the kidneys and other internal organs.
The analysis itself includes an assessment of the physicochemical characteristics of the studied biological fluid (urine), as well as a microscopic examination of the sediment.
The purpose of collecting urine for research is diagnostic, it consists in obtaining reliable results:
 Setting a siphon enema
Setting a siphon enema
The setting of a siphon enema is carried out in order to most effectively free the intestines from feces, gases, decay and fermentation products. Siphon enema also helps in the diagnosis of intestinal obstruction.
Indications for the procedure:
- Lack of proper effect from setting a cleansing enema .
- Removal of toxins, fecal, mucous, purulent contents from the intestinal cavity.
- Conditions accompanied by excessive processes of fermentation and putrefaction in the intestines.
- Severe flatulence.
- Preparation for surgical intervention on the intestines.
- Suspicion of intestinal obstruction.
 Emergency notification of infectious disease
Emergency notification of infectious disease
To prevent the spread of infections, according to the Order of the USSR Ministry of Health dated 04.10.80 N 1030, there is an “Emergency notification of an infectious disease” - an operational accounting document. Official registration form No. 058 / y, full name - "Emergency notification of an infectious disease, food, acute occupational poisoning, unusual reaction to vaccination."
Each case of an infectious disease or suspicion of it, pediculosis, poisoning or an unusual reaction to a vaccination must be transferred to the sanitary and epidemiological surveillance authorities. A notification is submitted no later than 2 hours after the discovery of the case. The sooner the notification is given, the easier it will be to take measures to prevent the spread of infection.
 Gastric lavage technique
Gastric lavage technique
Gastric lavage is carried out both for therapeutic and diagnostic purposes. This probe procedure is based on the principle of communicating vessels and serves to pump out the contents from the stomach. The technique of gastric lavage requires concentration, knowledge of anatomy and physiology, and skills in manipulating the phantom from the nurse.
Indications for gastric lavage
- Poisoning by ingested poisons, alcohol, drugs, other toxic agents.
- Food poisoning.
- Gastric pathologies, including gastritis, with abundant mucus formation.
- Diagnosis of oncological diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Identification of the pathogen in inflammatory processes in the stomach, as well as in the lungs and bronchi, when the patient cannot collect sputum.
 Vital capacity measurement
Vital capacity measurement
In order to assess the functional state of the respiratory system, the vital capacity of the lungs is measured using a special device - a spirograph.
Vital capacity (VC) is a value equal to the volume of air that the patient can exhale after taking the deepest possible breath. VC characterizes the state of the external respiration apparatus, allows you to assess the physical development of children and adolescents, to diagnose various diseases.
The procedure for determining the vital capacity of the lungs is called spirography . Manipulation requires the nurse to have knowledge about the device and the principles of operation of the apparatus, as well as the skills of examining patients.
 Classification of bone fractures
Classification of bone fractures
A bone fracture is a partial or complete violation of their anatomical integrity, accompanied by damage to surrounding tissues and impaired function of the injured segment.
The modern classification of bone fractures is diverse and is based on many factors.
Determining the type of fracture plays an important role in how correctly first aid will be provided, especially at the prehospital stage.
 Suture removal technique
Suture removal technique
To fix and hold the edges of the wound in surgery, suturing is used. After 5-7 days, the skin sutures must be removed, that is, the suture material must be removed. This manipulation is carried out according to the doctor's prescription and under his control. The technique for removing sutures is not particularly difficult, but requires the nurse to be attentive, dexterous and follow all the rules of asepsis and antisepsis.
 Wound classification
Wound classification
A wound is a mechanical damage (defect) of the skin, mucous membranes, underlying tissues and internal organs that occurs due to external influences. The modern classification of wounds is carried out according to several factors, which we will analyze below. The classic signs of an immediate establishment of the presence of a wound, in addition to damage to the skin and mucous membranes:
- pain;
- bleeding;
- hiatus.
 Applying a cold compress
Applying a cold compress
The setting of a cold compress or lotion is used to reduce pain, to prevent the spread of hematomas and to reduce body temperature during fever.
Indications for cold compresses:
- the first hours after bruises and other injuries;
- nose bleed;
- second period of fever;
- inflammatory processes in the mammary glands;
- acute inflammatory processes in the mammary glands;
- hematomas.
Contraindications
- Diabetes.
- Skin diseases.
- Cold intolerance.
- Chills (it is necessary to wait until the patient is completely warm).
The setting of cold compresses and lotions is carried out according to the doctor's prescription. Unlike warm compresses, cold compresses do not close.

 The setting of a siphon enema is carried out in order to most effectively free the intestines from feces, gases, decay and fermentation products. Siphon enema also helps in the diagnosis of intestinal obstruction.
The setting of a siphon enema is carried out in order to most effectively free the intestines from feces, gases, decay and fermentation products. Siphon enema also helps in the diagnosis of intestinal obstruction.