Methods of functional diagnostics
Methods of functional diagnostics
An objective assessment of the work of various organs and systems of the body can be made by methods of functional diagnostics - the study of functions with the help of technical instruments and apparatus. Functional diagnostics helps to establish the degree of disruption in the functioning of organs and systems. Functional abilities are examined in both adults and children.
Modern medicine cannot be imagined without this section. To work in the departments and cabinets of functional diagnostics, paramedical workers who have passed the relevant specialization and have successfully completed all the examination requirements are allowed.
There are many methods by which the physiological parameters of the human body are assessed. Let's consider the most common.
Methods of functional diagnostics in cardiology
Electrocardiography (ECG)
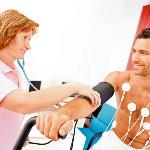
The main functional diagnostic method in cardiology. With the help of an ECG, a study of the activity of the heart is carried out both in the norm and in the presence of pathology. The basis of the method is the registration and analysis of the electrical activity of myocardial cells. The registration itself is carried out using special devices - electrocardiographs. The resulting recorded ("recorded") curve is an electrocardiogram - a graphical reflection of the dynamics of the potential difference at the points of application of two electrodes (positive and negative).
These electrodes are arranged in a certain way. Their mutual arrangement is called the electrocardiographic lead. When recording an ECG, 12 leads are used: 3 standard and 3 enhanced unipolar limb leads and 6 unipolar chest leads.
Recording an electrocardiogram helps to diagnose and monitor the following conditions in dynamics:
- myocardial infarction,
- changes in the work of the heart with rheumatism;
- heart defects;
- ischemic heart disease;
- hypertonic disease;
- all types of arrhythmias;
- other pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
Holter monitoring (HM-ECG)
24-hour Holter monitoring of the heart is a continuous ECG recording for 24 hours. This method of electrocardiography allows you to track the work of the heart not only at rest, but also under various loads - both physical and psychological.
Electrodes are applied to the patient's body, the ECG recorder is mounted on the chest, on the shoulder, or simply worn by patients in a small bag over the shoulder. The patient keeps a diary of his actions by time - sleeping, eating, climbing stairs, business negotiations, etc. The patient should be informed that he should lead his most normal life.
XM-ECG is widely used for difficulties in diagnosing arrhythmias, as well as for evaluating antiarrhythmic therapy.
Bicycle ergometry (treadmill testing)
The treadmill test is an electrocardiogram recording using increasing stepwise physical activity, which the patient receives on a bicycle ergometer. This special exercise bike doses the intensity of the load very accurately. The ECG is recorded in 12 leads (modified Mason-Likar leads).
This method is used in the diagnosis of coronary artery disease and arrhythmias, and is also a stress test for valvular heart disease and conditions after myocardial infarction.
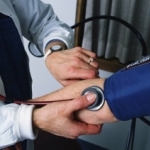
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM)
A method in which a portable portable machine records the patient's blood pressure and heart rate over a 24-hour period. ABPM allows you to identify "white coat hypertension", to evaluate ongoing antihypertensive therapy. The method is applied under the following conditions:
- borderline increase in blood pressure;
- newly diagnosed increase in blood pressure;
- combination of GB with coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular pathology - in order to identify critical thresholds for increasing blood pressure;
- arterial hypononia;
- syncope, or fainting in history.
Methods of functional diagnostics in neurology
Electroencephalography (EEG)
A method based on the registration and analysis of the bioelectrical activity of brain cells. For the study, electrodes are placed on the patient's scalp. When recording an electroencephalogram, tests are performed with closing the eyes, irritation with light and sound, hyperventilation (the patient is asked to take several deep breaths and exhalations).
The purpose of the study is to identify epilepsy, aneurysms, hematomas, tumors and other pathologies of the brain. EEG is used for panic attacks, poisoning, hysteria, and also to assess the maturity of the cerebral cortex in children.
Electroneuromyography (ENMG)
A method that allows you to study the electrical activity of muscles. ENMG helps to determine and evaluate the speed of the impulse along the nerve fiber. This method is used to diagnose the pathology of the peripheral nervous system and diseases such as myasthenia gravis, myopathy, myoclonus, amyopathic lateral sclerosis, muscular dystonia. Electroneuromyography is indicated if the patient has the following complaints:
- muscle weakness;
- muscle spasms, cramps, twitching;
- limb weight loss.
Doppler ultrasound of the main arteries of the head (USDG MAG)
Method for studying the vascular blood flow of the brain. The method is based on changing the frequency of sound waves reflected from moving solid blood components.
UZDG MAG is a screening study indicated for suspected acute cerebrovascular accident (stroke), as well as for patients with complaints of headaches, pain in the extremities in the absence of pathology in the extremities themselves.
Duplex and triplex color scanning of the main arteries of the head
The most modern and informative method. Color scanning makes it possible to see both the vessels of the brain and the tissues surrounding them. The study is carried out using an ultrasound scanner. On the monitor, the lumen of the vessel can be shown in both longitudinal and transverse directions, which makes it possible to assess both the state of the lumen and the vessel wall, and the direction and speed of blood flow.
Duplex and triplex scanning helps to identify stenoses and blockages, as well as congenital vascular pathologies, to determine the influence of the spine on the state of the vertebral arteries.
Methods of functional diagnostics in pulmonology
Spirography
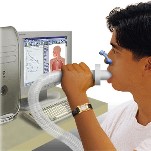
Spirometry is a method for assessing the function of external respiration (RF) using a special apparatus - a spirometer, spirography is a graphical reflection of the result of the study. The vital capacity (volume) of the lungs , airway patency, maximum ventilation and other indicators are determined With spirometry, respiratory function is assessed during quiet breathing, forced inhalation-exhalation, after exercise, and also after inhalation of a bronchodilator.
Spirography is indispensable in the diagnosis and evaluation of the results of treatment of bronchial asthma, pneumonia, bronchitis.
Peakflowmetry
A method for diagnosing and evaluating the results of treating bronchial asthma. It is carried out using a peak meter - a special graduated instrument. Peak expiratory flow is measured.
Pulse oximetry
The method is used as a rapid diagnosis of respiratory failure. It is carried out using a pulse oximeter, consisting of an electronic sensor fixed on the patient's finger and an electronic unit with a computer program. Pulse oximetry allows you to determine the oxygen saturation of hemoglobin in arterial and venous blood - saturation. Normal saturation of arterial blood is 95-100%.
We reviewed the most commonly used and effective methods of functional diagnostics of diseases used in cardiology, neurology and pulmonology. A functional diagnostic nurse is required to complete a specialization before starting work in this area.
Most of the FD methods are such that the procedure itself is carried out by a nurse, the doctor deciphers the result. In some studies, the presence of a doctor is necessary (treadmill test), some methods are performed by a doctor (doppler, ultrasound), a nurse assists and records.