Intramuscular injections
Intramuscular injections
Drugs entering the body, bypassing the gastrointestinal tract, are absorbed quickly and are not exposed to digestive juices. The injection method of drug administration is one of the preferred methods in the treatment of diseases. Therefore, any nurse should be able to perform injections intramuscularly
Of course, the more experience, the better any manipulation is performed. And in order to gain experience, injections should be given as often as possible to patients to whom they are prescribed. In the treatment rooms of any department of a hospital, dispensary, clinic, the technique of performing intramuscular injections is brought to perfection by nurses.
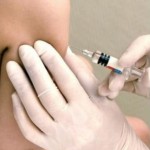
The most common site for intramuscular injection is the upper outer quadrant of any buttock. (Rarely - the upper third of the thigh, subscapular region). A quadrant is 1/4 of a circle. We conditionally accept the shape of one buttock as a circle, divide the circle into 4 parts and choose for intramuscular injection the quarter that is above and outside.
Before giving injections intramuscularly , intravenously or subcutaneously, the nurse changes into a uniform (gown or suit + cap or cap), puts on a mask and gloves.
Having determined the injection site, we draw the medicine into a syringe in compliance with all the rules of asepsis and antisepsis, in accordance with the sanitary and epidemiological regime.
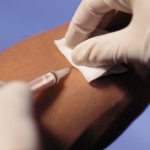
The patient lies on his side or stomach. If intramuscular injections are given in a standing position, the patient should focus on the leg that will NOT be injected. Thus, the muscles of the buttocks relax. We treat the injection site with a sterile cotton ball moistened with 70% alcohol twice. 1st treatment: lubricate the entire upper-outer quadrant, 2nd treatment: lubricate a smaller area of the skin - the one where we will inject.
We release air from the syringe. We put the syringe strictly perpendicular to the surface of the skin of the buttocks, about one centimeter from the injection site. With a sharp movement, we insert the needle into the muscle, but not to the cannula itself, but leave 2-3 mm above the skin surface. Holding the cannula of the needle, slowly press the plunger of the syringe.
After the injection of the drug, we press a sterile cotton swab moistened with alcohol to the puncture site of the skin. With a sharp movement, we remove the needle and press the cotton wool.
Before giving injections intramuscularly , the future nurse must work out the technique of setting intramuscular injections. For this, there is a special very convenient and visual simulator.
One half of the simulator is for practice, the other is for theory. After all, a nurse must know anatomy in order to prevent such complications of intramuscular injections as damage to nerves and large blood vessels.